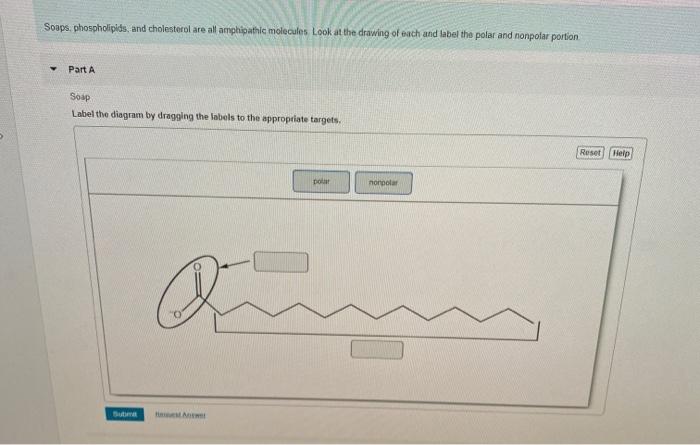
41 label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids
what part of a phospholipid forms hydrophobic tails - Lisbd-net.com Phospholipids have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions in a single molecule. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic because it is polar, enabling it to form hydrogen bonds with water. IN CONTRAST, the two long fatty acid tails are hydrophobic because they are nonpolar and do not form hydrogen bonds with water. Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Phospholipid Structure Labeling. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Solved Phospholipid labeling Label the parts of the | Chegg.com Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (14 ratings) Transcribed image text: Phospholipid labeling Label the parts of the phospholipid. Previous question Next question.
Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids
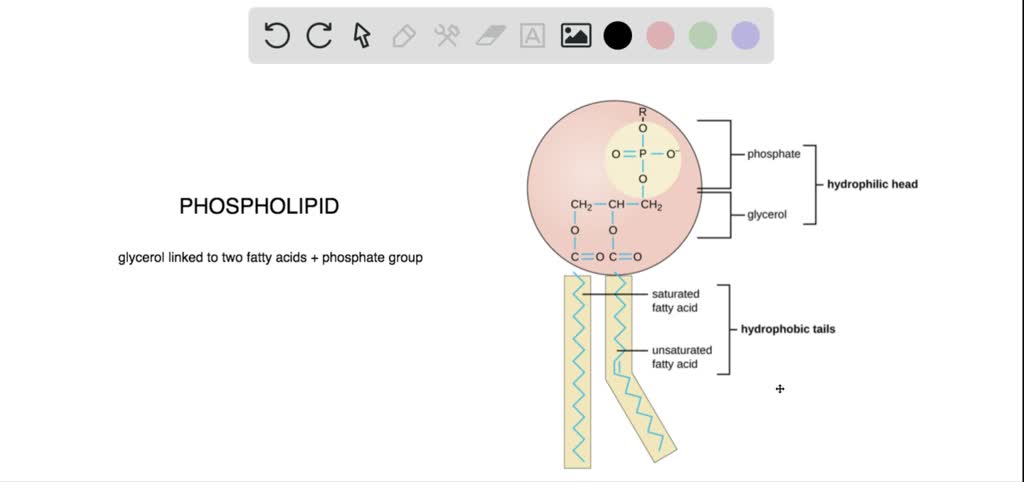
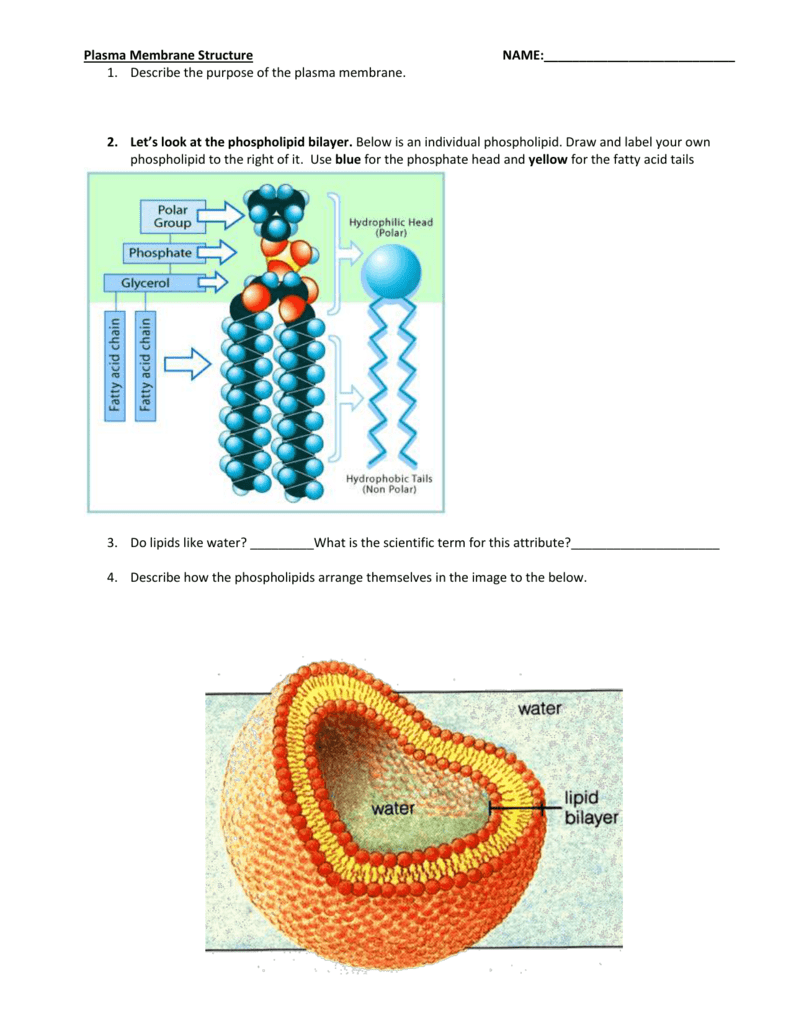
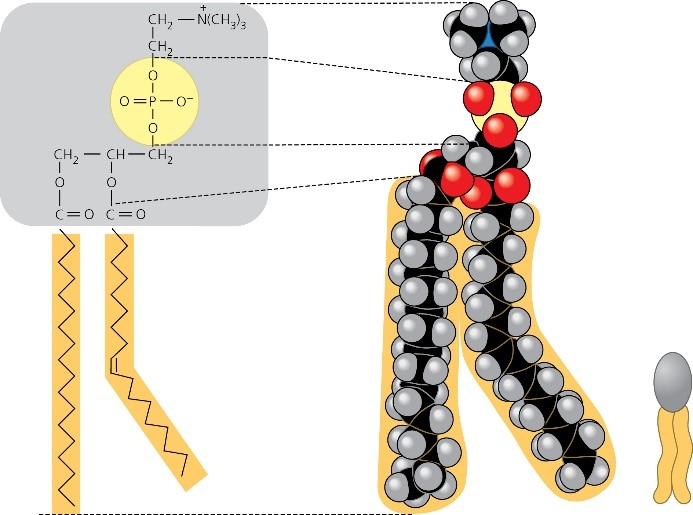
How a Phospholipid Bilayer Is Both Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic A phospholipid is named for its two main parts, a phosphate group and a lipid. It's usually drawn with the phosphate group as a circle, and this is referred to as the hydrophilic head. Due to its... Measurement of antioxidant activity - ScienceDirect 01.10.2015 · Unsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids and cholesterol, especially LDL-cholesterol, are generally the major reactants affected by such reactions, causing irreversible cellular and tissue damage. Oxidation of lipids may be via autoxidation, photooxidation, thermal oxidation and enzymatic oxidation, most of which involve free radicals and/or other reactive … Phospholipids - Structure, Types, Properties and Function A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components. A single phospholipid molecule is made up of a phosphate group on one end, referred to as the "head," and two side-by-side chains of fatty acids, referred to as the "tails."
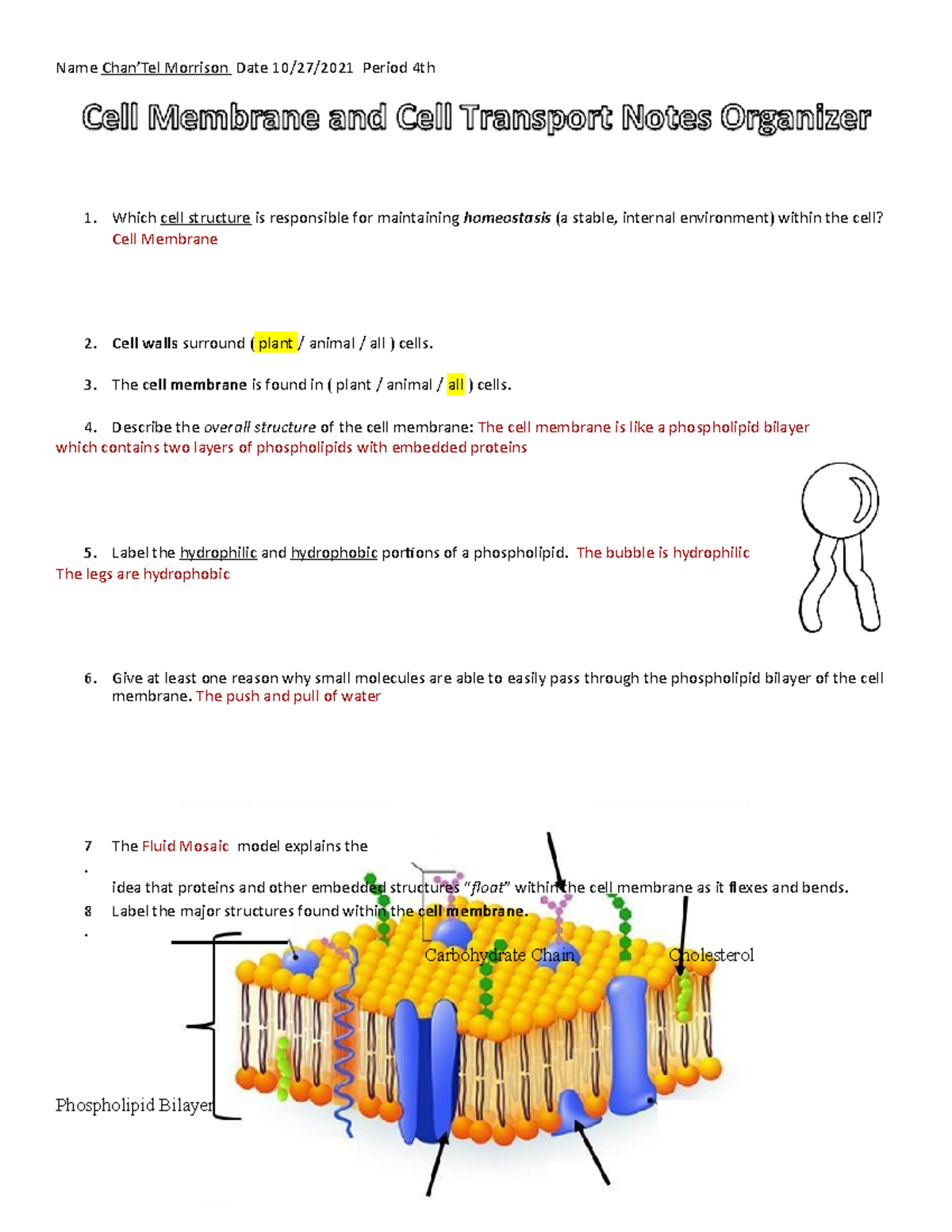
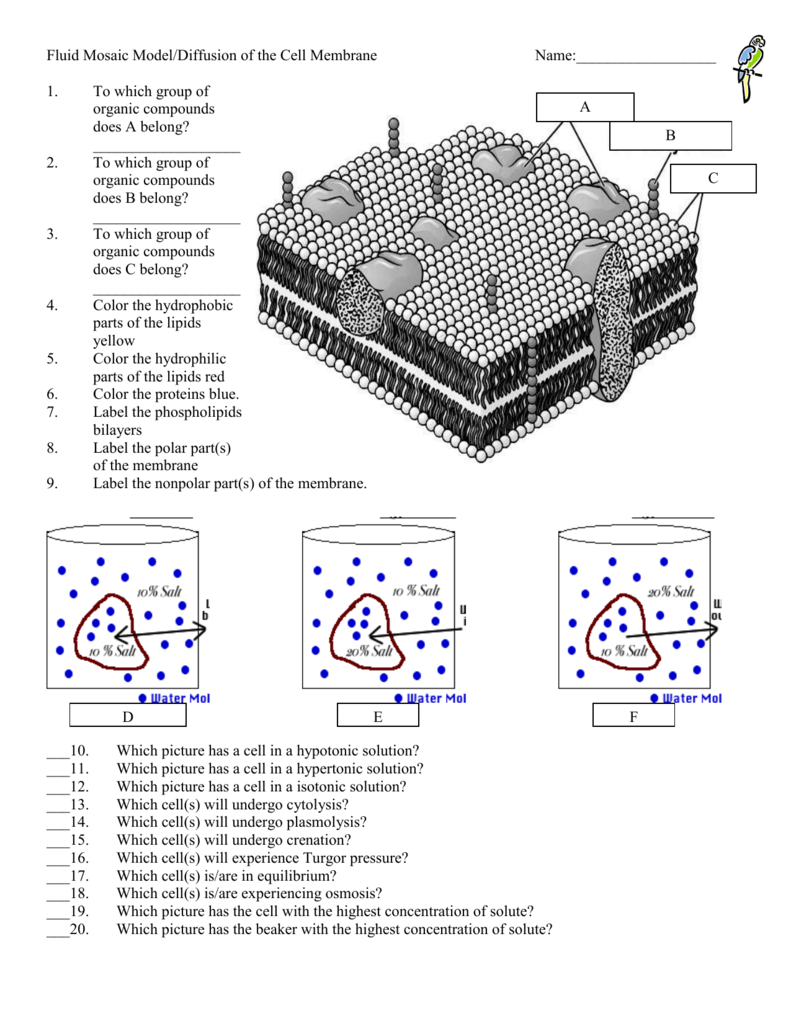
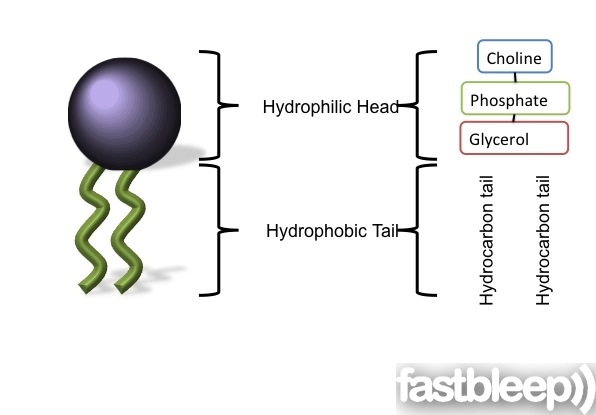
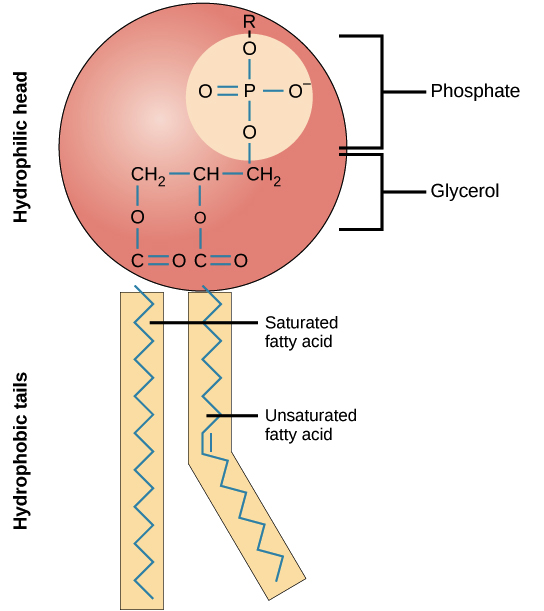
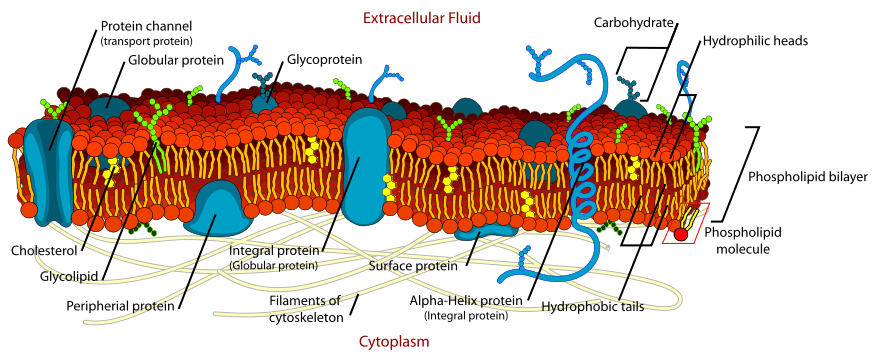
Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. Chapter 6. Lipids - Introduction to Molecular and Cell Biology The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups. A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic part. The "head" is composed of the hydrophilic phosphate group, and the "tail" contains the hydrophobic fatty acids. Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function, Examples - Science Terms A phospholipid consists of two basic parts: the head and the tail. The hydrophilic head consists of a glycerol molecule bound to a phosphate group. These groups are polar and are attracted to water. The second group, the hydrophobic tail, consists of two fatty acid chains. Some species use three fatty acid chains, but two is most common. Is cholesterol a hydrophobic or a hydrophilic substance? Cholesterol is an amphipathic molecule like phospholipids, it contains a hydrophilic and a hydrophobic portion. Its hydroxyl (OH) group aligns with the phosphate heads of the phospholipids. The remaining portion of it tucks into the fatty acid portion of the membrane. Emily approved September 8, 2017. Write your answer. Solved Match the cell membrane structure or its function - Chegg Question: Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the diagram Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids.
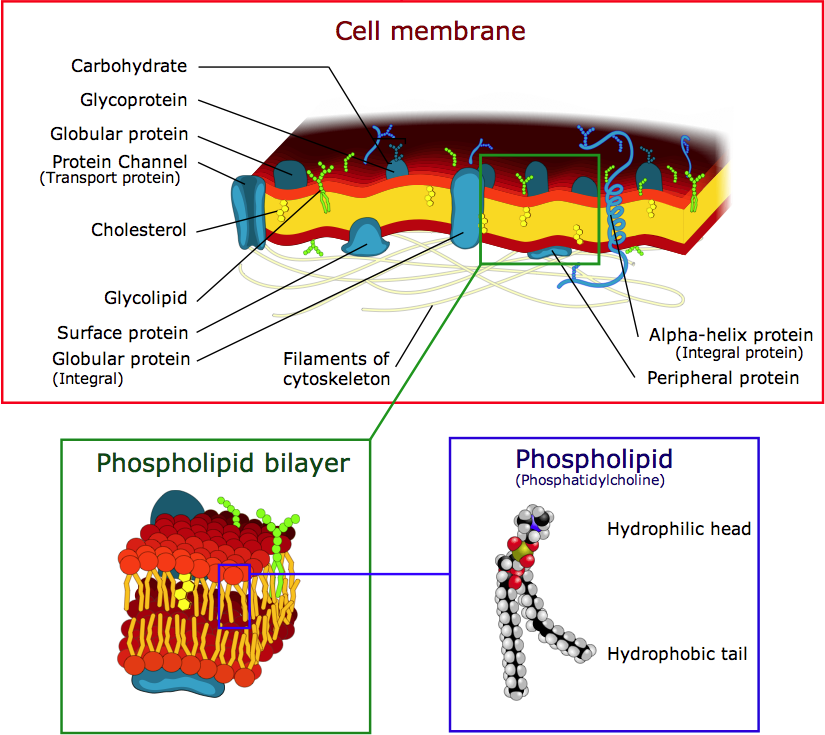
Phospholipid: Definition, Structure, Function - Biology Dictionary Hydrophobic - a molecule that "hates water"; it is not attracted to water, but will usually dissolve in oils or fats. Lipid bilayer - a double layer of phospholipids that makes up the cell membrane and other membranes, like the nuclear envelope and the outside of mitochondria. Quiz 1. Which is NOT a component of a phospholipid? A. Glycerol Phospholipid Structure & Function | What is a Phospholipid? Phospholipids have both a hydrophobic tail and a hydrophilic head. Hydrophobic means water fearing, in other words, the fatty acid tail (the hydrophobic portion of the phospholipid) does not mix... PDF Name Date Per Cell Membrane Structure and Function Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. Match the cell membrane structure or its function with the correct letter from the diagram. _____ Attracts water _____ Repels water _____ Helps maintain flexibility of membrane _____ Makes up the bilayer (2 answers) _____ Involved in cell-to-cell recognition Cambridge International AS and A Level Biology Coursebook … Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
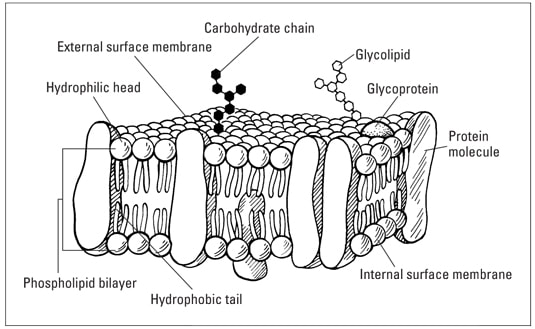
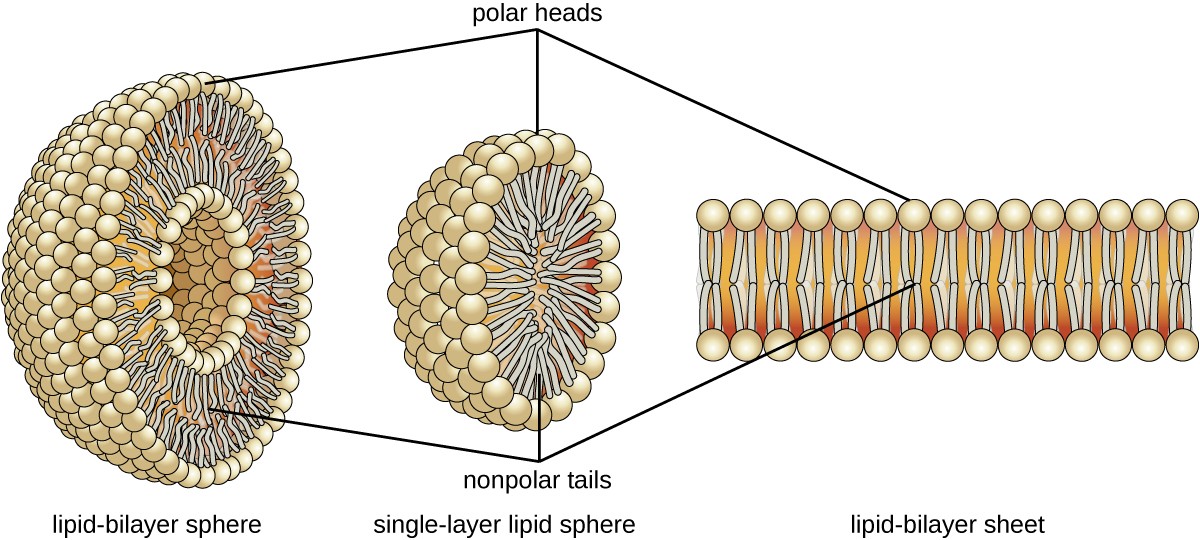
Phospholipid - Wikipedia Phospholipids, [1] are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids typically have omega-3 fatty acids EPA and DHA integrated as part of the phospholipid molecule. [2] Fennema's Food Chemistry 4th edition .pdf - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link. How Phospholipids Help Hold a Cell Together - ThoughtCo Phospholipids are a major and vital component of cell membranes. They form a lipid bilayer. In the lipid bilayer, the hydrophillic heads arrange to face both the cytosol as well as the extracellular fluid. The hydrophobic tails face away from both the cytosol and extracellular fluid. Phospholipids differ in size, shape, and chemical makeup. phospholipid | biochemistry | Britannica This amphipathic nature (containing both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups) makes phospholipids important in membranes; they form a two-layer structure, called the lipid bilayer, with the polar head facing out on each surface to interact with water, and with the neutral "tails" driven inward and pointing toward one another.
Phospholipids - Types, Functions and their Properties - An Overview - BYJUS Phospholipids are compound lipids, consisting of phosphoric acids, nitrogen base, alcohol and fatty acids. These compound lipids are major components of the cell membrane and also provide a fluid character to the membranes. In cell membranes, these phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail, which forms the inside of the bilayer.
Answered: Identify the hydrophobic and… | bartleby Solution for Identify the hydrophobic and hydrophilic region(s) of a phospholipid. close. Start your trial now! First week only $4.99! ... draw the structure of phospholipids. ... Label which end is polar and which one is nonpolar. Identify which end is known as being hydrophobic and which end is known as being hydrophilic. arrow_forward.
Biochemistry PDF | PDF | Cell (Biology) | Biochemistry This makes them amphiphilic molecules (having both hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions). In the case of cholesterol, the polar group is a mere -OH (hydroxyl or alcohol). In the case of phospholipids, the polar groups are considerably larger and more polar, as described below. Lipids are an integral part of our daily diet. Most oils and milk products that we use for cooking …
Patent 2946003 Summary - Canadian Patents Database All documents, or portions of documents, cited in this application, including, but not limited to, patents, patent applications, articles, books, and treatises, are hereby expressly incorporated-by-reference for the portions of the document discussed herein, as well as in their entirety. 17 CA 02946003 2016-10-14 WO 2015/168589 PCT/US2015/028837 Definitions Unless specific …
SOLVED:15. Phospholipids are found in cell membranes: the function of ... So the causes the amphitheater patting nature. Forceful leopards from the bi layer structure with the increase of the hydrophone or Philip lies outside and interact with the english environment whereas the hydrophobic steel and clusters and say For the question # 17, we have to label the given Diagram. So for this this portion is polar.
Phospholipid Bilayer | Introduction, Structure and Functions What Do Phospholipids Do Phospholipids perform various process inside the organisms. Fatty acids have the ability to form Cell Membranes because the Head of Phosphate group is Hydrophilic. While in contrast, the tails of Fatty Acid tails are Hydrophobic. Hydrophilic is the water-loving while Hydrophobic is water-hating molecules.
Lipid-Based Nanoparticles as Pharmaceutical Drug Carriers: From ... These liposomes 63 are based on the principle of photo-polymerization of lipids, 80 photo-sensitization by membrane-anchored hydrophobic probes, 72, 73, 81 – 83 or photo-isomerization of photo-reactive lipids. 84 The design principles and mechanisms of light-triggered chemical changes in photo-reactive segments of these lipids have been recently reviewed in detail.
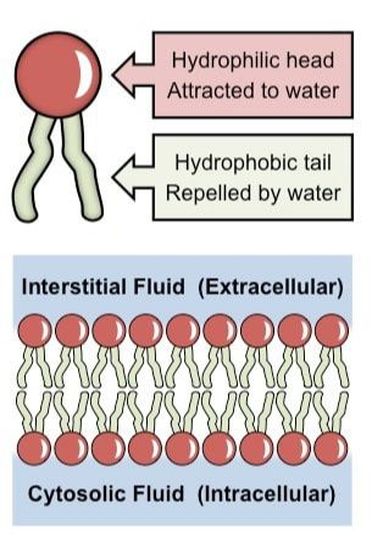
Correct Phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails The ... This self-assembly occurs because phospholipids are hydrophilic at one end (the phospholipid head) and hydrophobic at the other end (the phospholipid tails). Drag the labels to their appropriate locations in the figure. 1. First, drag labels to targets (a) and (b) to indicate whether these environments are hydrophilic or hydrophobic. 2.
Biology Quiz For Monday, October 1rst Flashcards | Quizlet Label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids. (know which is which) attracts water. hydrophilic. repels water. hydrophobic. Helps maintain flexibility of membrane. cholesterol. Makes up the bilayer (2 answers) A hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails.
The Lipid Bilayer - Molecular Biology of the Cell - NCBI Bookshelf The lipid bilayer has been firmly established as the universal basis for cell-membrane structure. It is easily seen by electron microscopy, although specialized techniques, such as x-ray diffraction and freeze-fracture electron microscopy, are needed to reveal the details of its organization. The bilayer structure is attributable to the special properties of the lipid molecules, which cause ...
Phospholipid Bilayer | Lipid Bilayer | Structures & Functions Fluid Mosaic Model (Source: Link). As its name implies, the phospholipid bilayer is made up of many phospholipids that lined up altogether. As shown in the diagram above, the bilayer is composed of hydrophilic (water-loving) heads that interact with the water on the outside environment, and a hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails that face each other in the inner structure of the membrane.
Biology Exam Review Flashcards | Quizlet Other substances are not attracted to water - they are hydrophobic. Phospholipids are unusual because part of a phospholipid molecule is hydrophilic and part is hydrophobic. Substances with this property are described as amphipathic. The hydrophilic part of a phospholipid is the phosphate group. The hydrophobic part consists of two hydrocarbon ...
10 draw and label a phospholipid show the hydrophobic - Course Hero Label this diagram of the plasma membrane with the following terms:glycoprotein,cholesterol, hydrophilic region, hydrophobic region. Phospholipid bilayer, protein molecules. a. hydrophobic regionb.hydrophilic regionc.phospholipid bilayerd.cholesterole.protein moleculesf.protein End of preview. Want to read all 2 pages?
What Part Of A Phospholipid Forms Hydrophobic Tails Phospholipids have both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions in a single molecule. The phosphate head group is hydrophilic because it is polar enabling it to form hydrogen bonds with water. IN CONTRAST the two long fatty acid tails are hydrophobic because they are nonpolar and do not form hydrogen bonds with water.
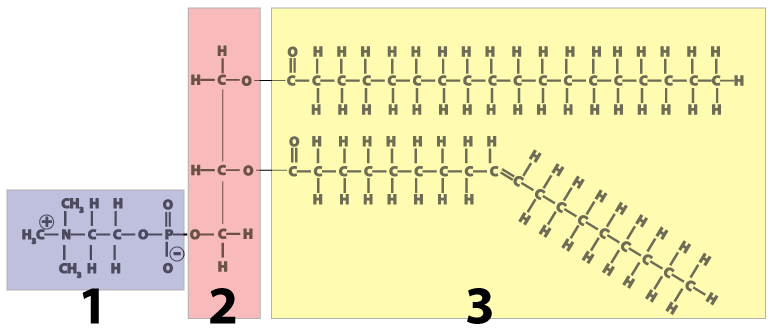
Glycerophospholipid - Wikipedia The phosphate ester portion ("head") is hydrophilic, whereas the remainder of the molecule, the fatty acid "tail", is hydrophobic. These are important components for the formation of lipid bilayers. Phosphatidylethanoamines, phosphatidylcholines, and other phospholipids are examples of phosphatidates. Phosphatidylcholines
(PDF) Thin Layer Chromatography - ResearchGate Feb 11, 2014 · Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a quick, sensitive, and inexpensive technique used to determine the number of components in a mixture, verify the identity and purity of a compound, monitor the ...
(Solved) - Which of the following statements is TRUE of ... - Transtutors Draw a membrane that includes ...
Phospholipids - Structure, Types, Properties and Function A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic components. A single phospholipid molecule is made up of a phosphate group on one end, referred to as the "head," and two side-by-side chains of fatty acids, referred to as the "tails."
Measurement of antioxidant activity - ScienceDirect 01.10.2015 · Unsaturated fatty acids in membrane phospholipids and cholesterol, especially LDL-cholesterol, are generally the major reactants affected by such reactions, causing irreversible cellular and tissue damage. Oxidation of lipids may be via autoxidation, photooxidation, thermal oxidation and enzymatic oxidation, most of which involve free radicals and/or other reactive …
How a Phospholipid Bilayer Is Both Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic A phospholipid is named for its two main parts, a phosphate group and a lipid. It's usually drawn with the phosphate group as a circle, and this is referred to as the hydrophilic head. Due to its...






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)
















Post a Comment for "41 label the hydrophobic and hydrophobic portions of the phospholipids"